主题: Photoelectron Spectroscopy Analysis of Ferroelectric Surfaces主讲人: Nicholas Barrett地点: 松江校区2号学院楼331报告厅时间: 2016-10-10 13:30:00组织单位: 理学院
主讲人简介:Nicholas Barrett, senior researcher at CEA/IRAMIS/SPEC, defended a PhD in Applied Physics from the University of Strathclyde (GB) in 1987. He joined the CEA in 1990 and in 1996 became manager of the CEA photoemission beamline on the SuperACO-LURE synchrotron. In 2005, he obtained the “Habilitation à Diriger des Recherches” from the University Pierre and Marie Curie (Paris). Head of the LENSIS laboratory, he has been involved in multiple national and European projects. He has a long experience in photoelectron spectroscopy using synchrotron radiation (Daresbury SLS, LURE, ESRF, ELETTRA, BESSY, SOLEIL, ANKA, SLS-Villigen, PETRA-III). Current research themes cover functional oxide electronic structure, surface and interface chemistry, ferroelectric and multiferroic films. He is author of 110 refereed scientific papers. He is PI of the CEA PEEM project, MesoXcopy, a new generation PEEM, optimized for spatially resolved band structure analysis, in Saclay, at ELETTRA and at the Attolab Equipex project using ultra-fast laser sources.
内容摘要:Photoelectron spectroscopy is powerful tool for the study of the chemistry and electronic structure of surfaces and interfaces. Functional oxides such as ferroelectrics represent one important challenge from both a fundamental interest and also with a view to their use as novel electronic, electrochemical and electromechanical materials.
After an introduction to photoelectron spectroscopy and ferroelectrics, we present a study of the chemistry of the nanostructured phase at the surface of lead zirconium titanate PbZr0.2Ti0.8O3 (PZT) films synthesized by sol-gel method. Excess lead precursor is used to maintain the target stoichiometry. Surface nanostructures appear at 10% excess lead. Using the surface-sensitive, quantitative X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and glancing angle X-ray diffraction we show that the chemical composition of the nanostructures is ZrO1.82-1.89 rather than pyrochlore often described in the literature. The presence of a discontinuous layer of wide band gap ZrO1.82-1.89 could be of importance in determining the electrical properties of PZT-based metal-insulator-metal heterostructures.
We have then carried out operando hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopy of the top interface in a Pt/Ru/PZT(220nm)/Pt/TiO2/SiO2/Si metal-insulator-metal capacitance structure. Interface specific, polarization dependent components appear in both Pb and Zr core-level spectra. The Zr component appears correlated to the surface nanostructures of the PZT film whereas the Pb component may be ascribed to micro-phase separation. The effective screening length is 0.23 Å and the Schottky barrier height for electrons 1.5 (2.7) eV for upwards (downwards) pointing polarization, consistent with the electrical characteristics.
Finally, the principles of photoelectron emission microscopy (PEEM) will be presented. The ferroelectric stability as a function of temperature of piezo force microscopy written domains in PbZr0.2Ti0.8O3 has been studied using threshold PEEM. A Curie temperature of 490°C is recorded which is also dependent on the poling voltage.
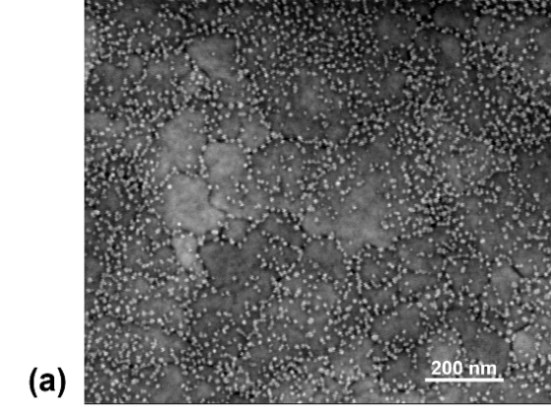
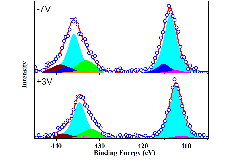
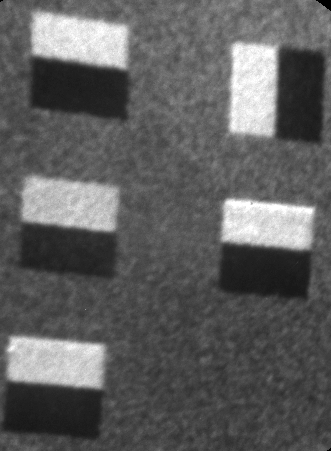
(left) nanostructures at the surface of sol-gel PZT ; (centre) coperando Pb 4d and Zr 3s core level spectra of electrode/PZT interface showing components which appear only under bias; (right) PEEM image of PFM-written domains in sol-gel grown PbZr0.2Ti0.8O3
讲座语言:英语